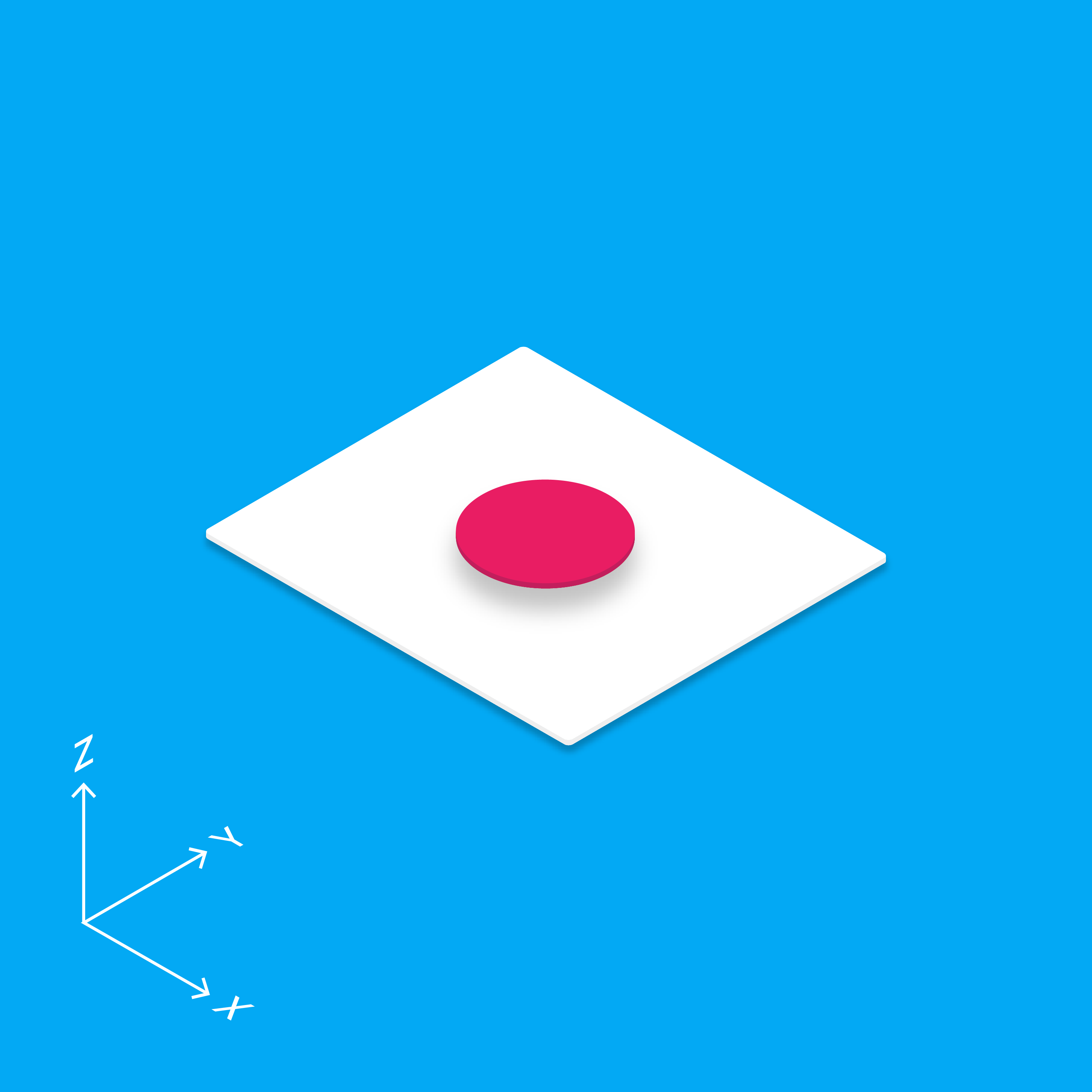
Material design is a three-dimensional environment containing light, material, and cast shadows.
All material objects have x, y, and z dimensions.
All material objects have a single z-axis position.
Key lights create directional shadows, and ambient light creates soft shadows.
Material thickness
1dp
Shadows
Shadows are created by the elevation difference between overlapping material.